

Why should traders use the Big Mac index? 3 Similarly, Bloomberg ran a Billy index, which converted the local prices of IKEA’s Billy bookshelf into US dollars and then compared the prices. The Economist has even produced variations of the Big Mac index, such as the Tall Latte index, which replaced the Big Mac with a Starbucks coffee. For example, the UBS Wealth Management and the Council of European Municipalities and Regions (CEMR) expanded the Big Mac index to look at how long the average employee in each country would have to work on minimum wage in order to buy a Big Mac. The concept of using hamburgers as an economic measure has become extremely popular, earning itself the title of ‘burgernomics’. If discrepancies are found, the theory would imply that the market will gradually correct itself and converge upon the same price point. If the theory of purchasing power parity holds true, then the price of a Big Mac should be identical in every country. 1 However, since its creation it has become used as a global standard of currency misalignment and is now published annually. The index was invented by The Economist in 1986, as a light-hearted measure of purchasing parity power. The idea is that if we compare each country’s price of a Big Mac against the US dollar, and calculate the Big Mac index exchange rate, we can establish whether currencies are over or undervalued against the dollar. The Big Mac index takes PPP theory and narrows it down to a specific good: a McDonald’s hamburger. If there is a lasting disparity between the prices of a basket of identical goods across different countries, then it could create an opportunity for items to be bought in the country that sells it for the lowest price. PPP theory suggests that, in the long run, the exchange rate between two currencies should move toward a point of conversion – so that the prices of identical goods and services become the same. PPP is used to determine how much the rate of exchange between two paper currencies impacts what consumers pay for daily goods and services. If we assume that PPP exists between these two nations, then a basket of goods that is worth $10 in the U.S.
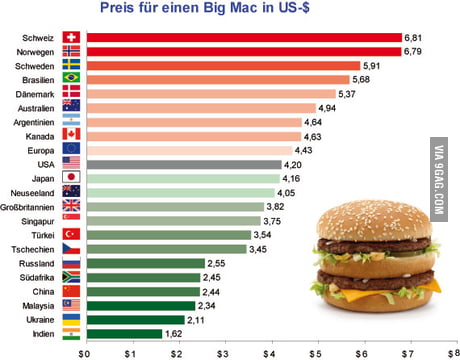
For example, suppose that the current exchange rate between Canada and the United States is 1.3 to 1, meaning that you’d need 1.30 Canadian dollars to buy one US dollar. It proposes that the price of a bundle of goods in one country should be equal to the price of that same bundle of goods in another country, once their currencies have been adjusted for the exchange rate. If the price of a Big Mac low then we can say that the prices in the country are low, even if the high prices are relatively high.Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a theory of exchange-rate determination. It also includes the cost of renting space and equipment, labor, and other factors. Big Mac contains meat, vegetables, cheese, bread and other foods. McDonald’s Menu Prices and Price List UK 2021 McDonald’s Prices UK McDonald’s BURGERS Individual Price Medium Extra Value Meal Large Extra Value Meal Big Mac 3.29 4.79 5.19 Quarter Pounder with Cheese 3.29 4.79 5.19 Double Quarter Pounder with Cheese 4.29 5.79 6.19 How is the price of a Big Mac determined?īig Mac index – the cost of a burger in McDonald’s network. 9 The Whole Euro Area Is Making It Big! How much does a Big Mac cost at McDonald’s? Average pizza prices were also very high in Umeå, Norrköping and Uppsala.Ī Big Mac in Sweden will cost you $5.83. Average pizza prices in pizzerias in Sweden in 2018, by city In 2018, consumers had to spent on average 84.89 Swedish kronor for a Vesuvio pizza from a pizzeria in Sweden’s capital Stockholm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
